Views: 0 Author: D and D Hardware Publish Time: 2022-08-18 Origin: D and D Hardware








Bored locks are installed in a door with two round holes bored at right angles to one another.
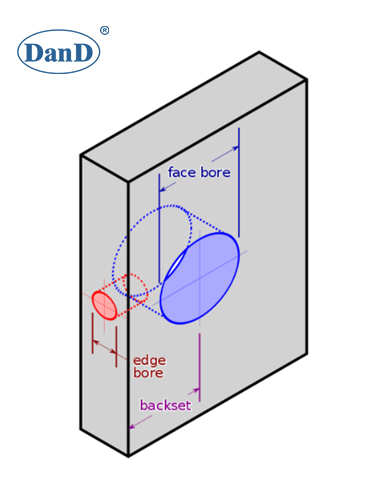
One hole is bored through the face of the door and is referred to as the cross bore/face bore; it holds the lock body.
The other hole is bored into the edge of the lock stile of the door and is referred to as the edge bore; the edge bore receives the latch-bolt assembly.
When bored locks are installed in the door, the lock body and latch-bolt assembly are interlocked together, forming a complete unit.
You might select bored locks over mortise locks for the following reasons:
Bored locks are less expensive,
easier and faster to install,
and have the key-in-the knob or key-in-lever feature.
However, they are not as durable as mortise locks.
Bored locks are designed to fit an industry-standard preparation.
For doors 1-3/4” or greater in thickness, the cross bore is 2-1/8” in diameter and is backset 2-3/4” from the long side of the beveled lock stile to the center of the preparation.
The cross bore is backset 2-3/8” for 1-3/8” thick doors. The edge bore is either 1” or 7/8” in diameter depending on the model of bored lock.
The area around the edge bore is typically mortised to receive the faceplate of the backset.
Construction:
There are two types of bored locks: Tubular and Cylindrical
Tubular lockset and latches have a latch-bolt assembly (a.k.a. backset assembly) that extends through the lock body when it is installed.
Cylindrical locks and latches have a latch-bolt assembly that interlocks with one side of the lock chassis.
Tubular locks are less expensive than cylindrical and are less durable.
A tubular lock might be used in a residential opening.
Grades:
Bored type locks are available in three BHMA grade categories:
Grade one – Heavy-duty
Grade two – Standard-duty
Grade three – Light-duty
In commercial buildings, grade one bored locks are used on openings of frequent use. For instance, the main entrance to a building or an office suite.
Grade two bored locks are used on openings of moderate use, such as an office or storage room door.
Grade three bored locks are usually reserved for interior doors such as in an apartment or similar dwellings and are also generally used in commercial applications.
Functions
The five most common bored lock functions are:
Passage, privacy, entrance, classroom and storeroom.
Passage: Latch bolt by inside or outside trim.
Privacy: Outside and inside trim retracts the latch-bolt, unless outside trim is locked by a button on the inside trim. Emergency key retracts the latch bolt when outside trim is locked. Inside trim always free for egress.
Entrance: Outside and inside trim retracts the latch bolt, unless outside trim is locked by a button on the inside trim. Key retracts the latch bolt when outside trim is locked. Inside trim always free for egress. Guard bolt deadlocks latch bolt.
Classroom: Outside trim locked or unlocked with a key.
Latch bolt by inside trim or key outside when locked. Inside trim always free for egress. Guard bolt deadlocks latch bolt.
Storeroom: Outside trim always rigid. Latch bolt by inside trim or key outside. Inside trim always free for egress. Guard bolt deadlocks latch bolt.
For further information about tubular lockset or any of our services, please click here.
Contact: David Jian
Mob: 0086-139 2903 7292
Email: sales@danddhardware.com